Tips for Drawaing Ray Diagram
- After refraction, a ray parallel to principal axis will pass through F.
- A ray passes through F, after refraction will emerge parallel to principal axis
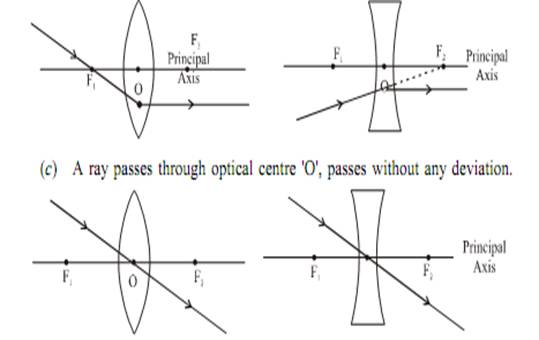
Image formation by a convex lens for various position of object
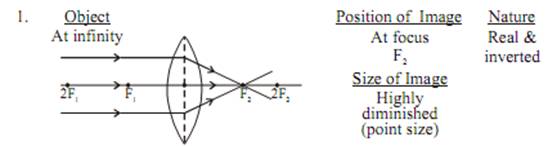
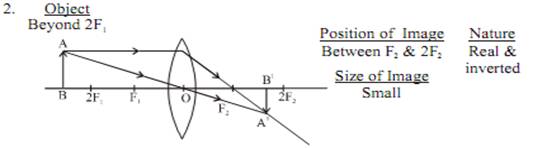
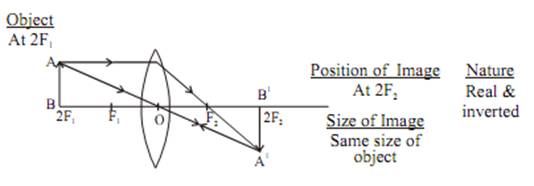
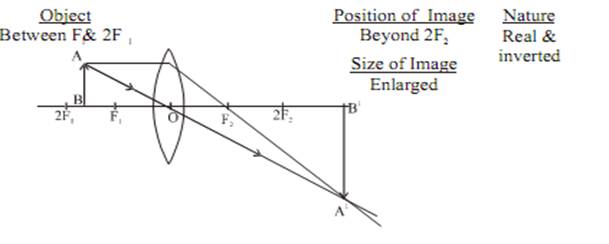
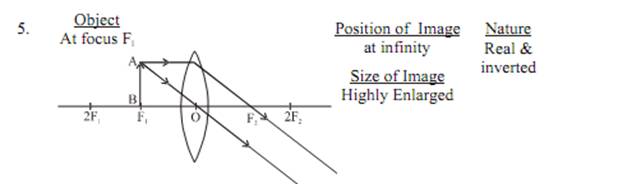
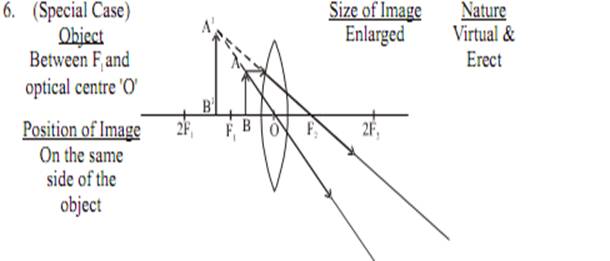
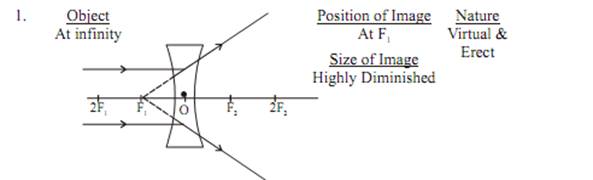
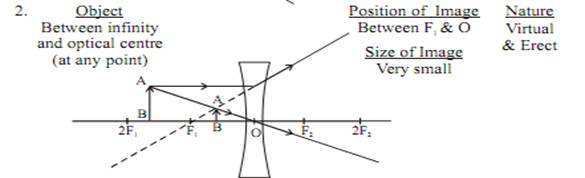
Image Formation by Concave Lens
Sign Convention for Refraction by Spherical Lens
Similar to that of spherical mirror, only the difference is that all themeasurement are made from optical centre ‘O’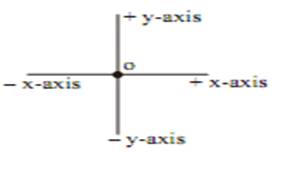
Lens formula
Magnification
It is defined as the ratio of the height of image to the height of object.
It is also related to ‘u’ & ‘v’
From equation (1) & (2)
If magnification
m > 1,then image is magnified
m = 1 ,image is of same size
m < 1, image is diminished
Few Tips to Remember Sign Convention for Spherical Lens
| f | u | v | |
| CONCAVE | -ve | -ve | -ve(virtual image always) |
| CONVEX | +ve | -ve | +ve(real) -ve(virtual) |
h is always +ve
h´ –ve for Real and +ve for Virtual &Errect.
Power of Lens
The degree of convergence or divergence of light ray achieved by a lensis known as power of a lens.
It is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length Represented by P.
If F is given in meter, then
If F is given in cm , then
SI unit of power of a lens is “diopter” denoted by ‘D’
I diopter or ID It is the power of lens whose focal length is I m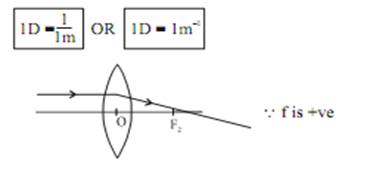
Power of convave lens or diverging lens is always negative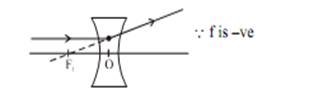
If any optical instrument has many lens, then net power will be
P= P1 + P2 + P3...

